HEALTH BENEFITS OF FERMENTED FOODS
Fermentation is an ancient form of food preservation, literally dating back several thousands of years in a variety of human cultures. It is caused by bacteria that create lactic acid via lacto-fermentation. (In Japan, this is known as Umami, or the fifth taste – tangy, tingly, and sour.)
Fermentation can occur in a variety of foods, for example:
cabbage → sauerkraut
soybean → miso
Even the olives that we buy at the store are fermented, making them palatable.
Fermentation is a natural form of “cooking” with several exciting health benefits. The key effect is to dramatically enhance the human immune system. A 2019 study by the University of Leipzig found that humans (and apes) but not other animals, possess receptors in the cells in their gut that recognize the bacteria in fermented food and respond by bolstering the immune system. Investigators theorize that this receptor might have developed as an evolutionary protection that allowed an ancestor to safely eat scavenged food found on the ground that may have begun to decay. In any case, the bottom line is that we have receptors to augment our immune system upon detection of lactic acid bacteria.
Australian scientist, Professor Kedgicska, recently reported work on the Novel Coronavirus in which they showed the human immune system responds to COVID-19 the same way as with the flu. This give confidence that an aggressive immune system response can prevent or mitigate the virus. While there is no vaccine for COVID-19 for probably another year, this means strengthening the immune system is the primary approach.
In a study at Georgia State University they showed the efficacy of fermented foods in protection against the flue strain H3N2. In a study, mice pretreated with lactic acid bacteria then injected with a lethal dose of the flu virus. The treated mice survived with 18x less viral bacteria in their lungs. The control group without LAB protection all died.
Of course, cultures with extreme experience with fermented foods have the most human testing experience. Korea uses Kimchi with nearly all meals. In a study conducted by the Korea Food Research Institute, they reached the following conclusions: “the bioactive compounds from lactic acid bacteria serve as antiviral agents and were effective against swine flue and A1 (Avian influenza) viruses.”
Fermentation also produces several key enzymes and B vitamins. For example, fermentation causes a 580% increase in thiamine and a 950% increase in niacin. B vitamins are key to cardiovascular health and many Americans today consume far less than the body needs.
Mental health improvements from eating fermented foods are due to the increase in “good” gut bacteria, which is driven by the lacto-bacteria. The gut, when populated by beneficial bacteria, produces more serotonin than the brain can. Serotonin is a key enzyme that helps to control mood and outlook.
Fermented foods are safe. The lacto-bacteria in fermented foods is potent and beneficial. For example, in food contaminated with the e-coli bacteria (a cause of many food poisoning outbreaks), the lacto-fermentation process will kill the e-coli, rendering the food safe to eat. As a matter of fact, in the 1950s German scientists successfully used sauerkraut (lacto-fermentation) to treat outbreaks of typhoid fever. More recently, scientists have shown that lacto-bacteria can potentially treat “super bugs,” a significant modern-day medical threat.
One of the most exciting health implications of fermented foods is for Type 2 Diabetes. The bacterial content of intestines differ markedly when comparing Type II diabetics to non-diabetic gut populations. This has several implications. Lactic acid and acetic acid help block the absorption of carbohydrates from rapidly converting to blood sugar, helping eliminate spikes.
Fermented foods help the digestive process by stimulating aceticholine which is a neurotransmitter that helps movement of the bowel, reducing constipation. It also improves the release of digestive juices and enzymes from the stomach, pancreas, and gallbladder. Thus, fermented foods are potent digestive aids. It, therefore, follows naturally that fermented foods have a big impact on acid reflux. This is a critical health issue in the United States now, with 60 million cases annually, or one in five people. It has long term health implications on a variety of concerns, including asthma.
Ironically, it is reported that acid reflux is caused by levels of stomach acid that are too low, allowing partially digested food and pathogens into the small intestines which leads to undesirable chemical processes that generate gases. These force the stomach acid past the valve at the top of the stomach up into the esophagus. Antacids neutralize the acid that has escaped, providing some relief but do not solve the underlying problem.
Normally the high acidity of the stomach kills harmful bacteria and pathogens in the area surrounding surfaces of the food that we eat. When the stomach acidity falls, harmful bacteria survives to bad outcomes. These bacteria enter the intestine where they produce methane and hydrogen which forces the lower esophageal valve to open and acid to flow back up into the esophagus. Low stomach acid interferes with the triggering mechanism of the valve. These bacteria interfere with proper digestion which provides more time for the gas production to continue. Lacto-fermented foods contain bacteria that fight the bad bacteria that considerably instigate acid reflux disease.
In general, the lacto-fermentation process greatly assists in controlling inflammation and augmenting the immune system, including helping suppress polyps relating to colon cancer, and even augmenting the immune system for HIV patients.
Fermented foods are “living” foods: an ancient process to fight modern-day food problems. The optimum way to maximize the health benefits is to consume small amounts of live-fermented foods with at least one meal a day, every day.
Some examples of fermented foods available are:
- Sauerkraut (used in German cooking)
- Fermented Dill Pickles (excellent tart taste)
- Fermented Carrots (fermented with ginger)
- Fermented Beets & Cabbage (a unique taste)
- Kimchee (used in Korean cooking)
- Fermented condiments and hot sauces
Learn about Arona Berries here!
Aronia berries, also known as black chokeberries, is a small black berry that is rapidly becoming known as the next superfood. It contains the highest concentration of anthocyanins, a phytochemical with demonstrated potential in the treatment of diabetes, heart disease and cancers.
Anthocyanin (ACN) Content
Aronia berries are extremely high in this phytochemical. Table 1
Table 1: ACN Concentration
Aronia 2147
Blueberry 533
Blackberry 353
Cherries 177
Onions 138
Red Raspberry 116
Eggplant 35
Red Beans 25
As seen above, dark berries such as Aronia and Blueberries are the most potent source of Anthocyanin (ACN).
Antioxidants (ORAC) Content
A similar impact is seen in the antioxidant properties of the Aronia berry.
Oxygen is essential to life, but there is a flip side. In the process of metabolizing oxygen, 1-2% of the molecules will turn into “free radicals” and these can damage cells. Free radicals can come from many elements of modern life: pollution, poor nutrition, or stress. This oxidative stress plays a part in the development of chronic and degenerative illnesses such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, aging, arthritis, and cardiovascular diseases. Antioxidants provide protection from free radicals and the DNA damage they can cause.
ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) values for Aronia berries are extraordinary. Table 2
Table 2: ORAC Values
Aronia berries 17,000
Blueberries 4,500
Strawberries 4,200
Non-Berry Fruit 1,000 – 2,500
Vegetables 250 – 2,000
The combination of stellar anthocyanin and superior antioxidant values are the basis of the berry’s impact on disease.
Cancer
With the breadth of anti-cancer studies of the aronia berry underway, the full impact will be defined in the future. A few examples will illustrate their potential.
In a study recently released by the Department of Natural Sciences at Middlesex University it was shown that the combination of aronia and curcumin were able to successfully stop the spread of malignant cells and induce apoptosis (death of the malignant cell). The cancer involved was brain cancer known as U373.
In another study, the effect of aronia berries on colon cancer cells showed that cancer cell proliferation was inhibited by 30-40% after administration of a final dose of aronia juice.
A laboratory study by physlotherapy research showed that anthocyanin extracts inhibited the growth of breast cancer.
Diabetes
Aronia berry’s primary impact on diabetes is its impact on the pancreas, helping to regulate the blood sugar levels. In one study, the daily intake of 200ml of aronia juice successfully caused a decreased glucose level in Type II diabetic patients. The anthocyanin also helped diabetic patients by successfully fighting the enzyme that dissolves collagen and elastins. This helps diabetic patients return to normal collagen levels. The high ORAC values of this berry minimize the damage that free radicals do to cause arterial wall damage. Thus, it can help prevent the metabolic syndrome that many diabetic patients suffer.
Heart Health
The effects of aronia berries on heart health is remarkable, probably due to its powerful effect on reducing systemic inflammation in the body.
In studies involving 100ml of aronia juice daily, the impact on LDL was -5.8. Longer term use elevated the HDL and had favorable impacts on c-reactive protein and triglycerides.
In a meta-analysis of data from UK, Iran, China India, and Nigeria, the broad impact of Aronia on heart health was demonstrated. The report will be made available to the public by December of 2019.
Anthocyanin Extraction
The key ingredient in the aronia is the phytochemical, anthocyanin. The problem is that anthocyanin is bound up in the skin of the aronia and blueberries and is barely available to the human. To solve this, the berries are frozen, causing micro-cracking in the skin thus making the anthocyanin more available.
Ways to Consume Aronia
Juice:
The simplest approach is to press the berries to make a juice. This is how the majority of aronia is consumed.
Chutney:
Another aronia product is Fermented Aronia Chutney. In this product, the previously frozen aronia is fermented for a short time (3-4 days). The lacto-bacteria extract the anthocyanin in a spread that can be used like jam (but without the sugar) as a healthy addition to your diet.
Kombucha:
A popular healthy drink is Kombucha. Aronia berries can be fermented in the kombucha process which makes a delightful drink.
Fermented Aronia Berries:
The ultimate way to produce the maximum anthocyanin content is to ferment the frozen, micro-cracked berries with lacto-bacteria. The trick is the time of fermentation. In blueberries, the fermentation time is limited to 3 days because the high natural sugar content encourages alcohol production. In the Aronia berry case, the berry contains a low level of sugar, so longer fermentation times are feasible.
* Experiments are ongoing and will be available in 2023.
Aronia berries offer a life-changing health benefit!
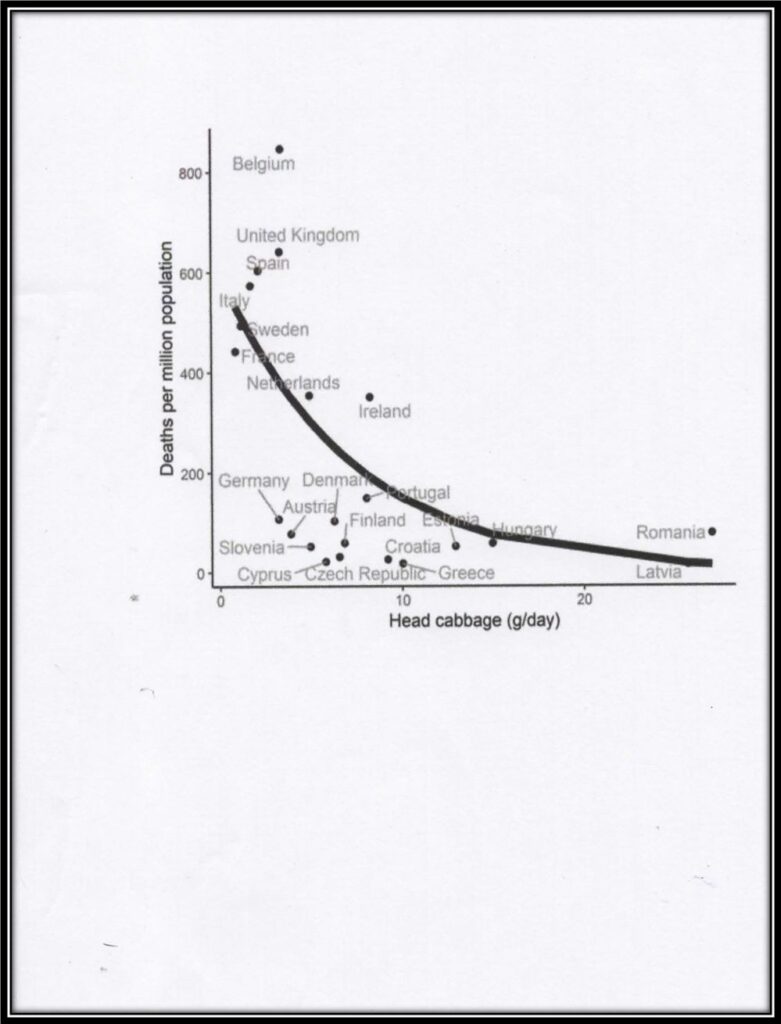
Covid-19 Mortality vs Cabbage Consumption